Build a UI with Layout Editor
The Layout Editor enables you to quickly build layouts by dragging UI elements into a visual design editor instead of writing layout XML by hand. The design editor can preview your layout on different Android devices and versions, and you can dynamically resize the layout to be sure it works well on different screen sizes.
The Layout Editor is especially powerful when building a layout with ConstraintLayout, a layout manager that's compatible with Android 2.3 (API level 9) and higher.
This page provides an overview of the Layout Editor. To learn more about layout fundamentals, see Layouts.
Introduction to the Layout Editor
The Layout Editor appears when you open an XML layout file.

Figure 1. The Layout Editor
- Palette: Contains various views and view groups that you can drag into your layout.
- Component Tree: Shows the hierarchy of components in your layout.
- Toolbar: Click these buttons to configure your layout appearance in the editor and change layout attributes.
- Design editor: Edit your layout in Design view, Blueprint view, or both.
- Attributes: Controls for the selected view's attributes.
- View mode: View your layout in either Code
 , Design
, Design  , or Split
, or Split  modes. Split mode shows both the Code and Design windows at the same time.
modes. Split mode shows both the Code and Design windows at the same time. - Zoom and pan controls: Control the preview size and position within the editor.
When you open an XML layout file, the design editor opens by default, as shown in figure 1. To edit the layout XML in the text editor, click the Code ![]() button in the top-right corner of the window. Note that the Palette, Component Tree, and Attributes windows are not available while editing your layout in Code view.
button in the top-right corner of the window. Note that the Palette, Component Tree, and Attributes windows are not available while editing your layout in Code view.
Tip: You can switch between design and text editors by pressing Alt + Shift + Right/Left arrow (Control + Shift + Right/Left arrow on Mac).
Change the preview appearance
The buttons in the top row of the design editor enable you to configure the appearance of your layout in the editor.
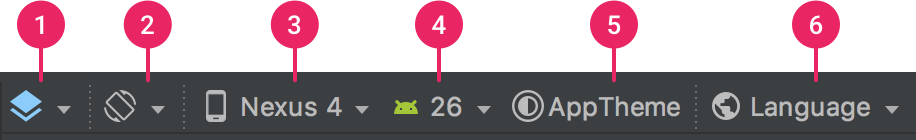
Figure 2. Buttons in the Layout Editor toolbar that configure the layout appearance
Corresponding to the numbers in figure 2, the buttons available are as follows:
- Design and blueprint: Select how you'd like to view your layout in the editor. Choose Design to see a rendered preview of your layout. Choose Blueprint to see only outlines for each view. Choose Design + Blueprint to see both views side-by-side. You can also press
Bto cycle through these view types. - Screen orientation and layout variants: Choose between landscape and portrait screen orientation, or choose other screen modes for which your app provides alternative layouts, such as night mode. This menu also contains commands for creating a new layout variant. You can also press
Oto change orientation. - Device type and size: Select the device type (phone/tablet, Android TV, or Wear OS) and screen configuration (size and density). You can select from several pre-configured device types and your own AVD definitions, or you can create a new AVD by selecting Add Device Definition from the list. You can resize the device size by dragging the bottom-right corner of the layout. You can also press
Dto cycle through the device list. - API version: Select the version of Android on which to preview your layout.
- App theme: Select which UI theme to apply to the preview. Note that this works only for supported layout styles, so many themes in this list result in an error.
- Language: Select the language to show for your UI strings. This list displays only the languages available in your string resources. If you'd like to edit your translations, click Edit Translations from the drop-down menu. For more information on working with translations, see Localize the UI with Translations Editor.
Note: Unless you choose to add a new layout file from Layout Variants, these configurations have no effect on your app's code or manifest. They affect only the layout preview.
Create a new layout
When adding a new layout for your app, first create a default layout file in your project's default layout/ directory so that it applies to all device configurations. Once you have a default layout, you can create layout variations for specific device configurations, such as for large screens.
You can create a new layout in one of the following ways:
Use Android Studio's main menu
- In the Project window, click the module in which you want to add a layout.
- In the main menu, select File > New > XML > Layout XML File.
- In the dialog that appears, provide the file name, the root layout tag, and the source set in which the layout belongs.
- Click Finish to create the layout.
Use the Project view
- Choose the Project view from within the Project window.
- Right-click the layout directory where you'd like to add the layout.
- In the context menu that appears, click New > Layout Resource File.
Use the Android view
- Choose the Android view from within the Project window.
- Right-click the
layoutfolder. - In the context menu that appears, select New > Layout Resource File.
Use the Resource Manager
- In the Resource Manager, select the Layout tab.
- Click the
+button, and then click Layout Resource File.
Use layout variants to optimize for different screens
A layout variant is an alternative version of an existing layout that is optimized for a certain screen size or orientation.
Use a suggested layout variant
Android Studio includes common layout variants that you can use in your project. To use a suggested layout variant, do the following:
- Open your original layout file, click the Design
 icon in the top-right corner of the window.
icon in the top-right corner of the window. - Click Orientation for Preview (
 ) in the toolbar.
) in the toolbar. - In the dropdown list, select a suggested variant, such as Create Landscape Variant.
Create your own layout variant
If you'd like to create your own layout variant, do the following:
- Open your original layout file, and click the Design icon (
 ) in the top-right corner of the window.
) in the top-right corner of the window. - Click Orientation for Preview
 in the toolbar.
in the toolbar. - In the dropdown list, select Create Other....
- In the dialog that appears, define the resource qualifiers for the variant. Select a qualifier from the Available qualifiers list, and then click the Add
 button. Repeat this step to add other qualifiers as needed.
button. Repeat this step to add other qualifiers as needed. - Once you've added all of your qualifiers, click OK.
When you have multiple variations of the same layout, you can switch between them by clicking Layout Variants  and choosing from the list that appears.
and choosing from the list that appears.
For more information about how to create layouts for different screens, see Supporting different screen sizes.
Convert a view or layout
You can convert a view to another kind of view, and you can convert a layout to another kind of layout.
- Click the Design button in the top-right corner of the editor window.
- In the Component Tree, right-click the view or layout, and then click Convert view....
- In the dialog that appears, choose the new type of view or layout, and then click Apply.
Convert a layout to ConstraintLayout
For improved layout performance, you should convert older layouts to ConstraintLayout. ConstraintLayout uses a constraint-based layout system that enables you to build most layouts without any nested view groups.
To convert an existing layout to a ConstraintLayout, do the following:
- Open an existing layout in Android Studio, and click the Design button in the top-right corner of the editor window.
- In the Component Tree, right-click the layout, and then click Convert
your-layout-typeto ConstraintLayout.
To learn more about ConstraintLayout, see Build a Responsive UI with ConstraintLayout.
Find items in the Palette
To search for a view or view group by name in the Palette, click the Search  button at the top of the palette. Alternatively, you can type the name of the item whenever the Palette window has focus.
button at the top of the palette. Alternatively, you can type the name of the item whenever the Palette window has focus.
You can find frequently used items in the Common category in the Palette. To add an item to this category, right-click on a view or view group in the Palette, and then click Favorite in the context menu.
Open documentation from the Palette
To open the Android Developers reference documentation for a view or view group, select the UI element in the Palette and press Shift + F1.
To view Material Guidelines documentation for a view or view group, right-click the UI element in the Palette and select Material Guidelines from the context menu. If no specific entry exists for the item, then the command opens the home page of the Material Guidelines documentation.
Add views to your layout
To start building your layout, simply drag views and view groups from the Palette into the design editor. As you place a view in the layout, the editor displays information about the view's relationship with the rest of the layout.
If you are using ConstraintLayout, you can automatically create constraints using the Infer Constraints and Autoconnect features.
Edit view attributes

Figure 3. The Attributes window
You can edit view attributes from the Attributes window on the right side of the Layout Editor. This window is available only when the design editor is open, so be sure you're using either Design or Split mode to view your layout.
When you select a view, whether by clicking the view in the Component Tree or in the design editor, the Attributes window shows the following, as indicated in figure 3:
The Declared Attributes section lists attributes specified in the layout file. To add an attribute, click the Add
 button at the top right of the section.
button at the top right of the section.The Layout section contains controls for the width and height of the view. If the view is in a
ConstraintLayout, this section also shows constraint bias and lists the constraints that the view uses. For more information on working withConstraintLayout, see Build a Responsive UI with ConstraintLayout.The Common Attributes section lists common attributes for the selected view. To see all available attributes, expand the All Attributes section at the bottom of the window.
Click the Search button to search for a specific view attribute.
The icons to the right of each attribute value indicate whether the attribute values are resource references. These indicators are solid
 when the value is a resource reference and empty
when the value is a resource reference and empty  when the value is hard-coded. These indicators help you recognize hard-coded values at a glance. Clicking indicators in either state opens the Resources dialog window where you can select a resource reference for the corresponding attribute.
when the value is hard-coded. These indicators help you recognize hard-coded values at a glance. Clicking indicators in either state opens the Resources dialog window where you can select a resource reference for the corresponding attribute.A red highlight around an attribute value indicates an error with the value. An error might indicate an invalid entry for a layout-defining attribute, as shown in the red highlight in figure 3.
An orange highlight indicates a warning for the value. A warning might appear when you use a hard-coded value where a resource reference is expected, for example.
Add sample data to your view
Because many Android layouts rely on runtime data, it can be difficult to visualize the look and feel of a layout while designing your app. In Android Studio 3.2 and later, you can add sample preview data to a TextView, an ImageView, or a RecyclerView from within the Layout Editor.
Note: When you add sample data to a View, Android Studio makes changes to your project as though you were using your own data. You can then modify these changes as needed.
You can right-click on one of these view types and choose Set Sample Data to display the Design-time View Attributes window, as shown in figure 4.

Figure 4. The Design-time View Attributes window
In a TextView, you can choose between different sample text categories. When using sample text, Android Studio populates the text attribute of the TextView with your chosen sample data. Note that you can choose sample text via the Design-time View Attributes window only if the text attribute is empty.

Figure 5. A TextView with sample data
In an ImageView, you can choose between different sample images. When you choose a sample image, Android Studio populates the tools:src attribute of the ImageView (or tools:srcCompat if using the Support Library).

Figure 6. An ImageView with sample data
In a RecyclerView, you can choose between a set of templates that contain sample images and texts. When using these templates, Android Studio adds a file to your res/layout directory, recycler_view_item.xml, that contains the layout for the sample data. Android Studio also adds metadata to the RecyclerView to properly display the sample data.

Figure 7. A RecyclerView with sample data
Show layout warnings and errors
The Layout Editor notifies you of any layout issues next to the corresponding view in the Component Tree by using a red circle exclamation icon  for errors or an orange triangle exclamation icon
for errors or an orange triangle exclamation icon  for warnings. Click on the icon to see more details.
for warnings. Click on the icon to see more details.
To see all known issues in a window below the editor, click Show Warnings and Errors ( or
or  ) in the toolbar.
) in the toolbar.
Download fonts and apply them to text
When using Android 8.0 (API level 26) or Android Support Library 26.0.0 or higher, you can select from hundreds of fonts by following these steps:
- In the Layout Editor, click the Design
 button to view your layout in the design editor.
button to view your layout in the design editor. - Click on a text view.
- In the Attributes window, expand textAppearance, and then expand the fontFamily box.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list and click More Fonts to open the Resources dialog.
- In the Resources dialog, select a font by browsing the list or by typing into the search bar at the top. If you select a font under Downloadable, then you can either click Create downloadable font to load the font at runtime as a downloadable font, or click Add font to project to package the TTF font file in your APK. Note that the fonts listed under Android are provided by the Android system, so they do not need to be downloaded or bundled in your APK.
- Click OK to finish.


0 Comments